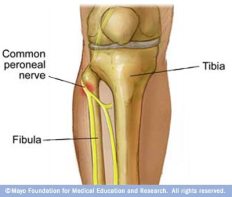
 The common peroneal nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the leg due to its superficial location where it courses laterally around the neck of the fibula. This location makes the common peroneal nerve susceptible to injury when a straumatic insult results in fracture of the neck of the fibula. The sciatic nerve branches into the common peroneal (fibular) nerve and the tibial nerve posteriorly on the thigh just proximal to the popliteal fossa. after coursing around
The common peroneal nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the leg due to its superficial location where it courses laterally around the neck of the fibula. This location makes the common peroneal nerve susceptible to injury when a straumatic insult results in fracture of the neck of the fibula. The sciatic nerve branches into the common peroneal (fibular) nerve and the tibial nerve posteriorly on the thigh just proximal to the popliteal fossa. after coursing around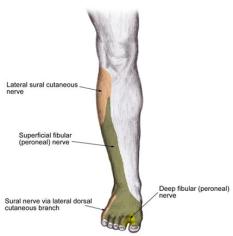 the neck of the fibula, the common peroneal nerve divides into superficial and deep branches. the superficial branch innervates the muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg, which function primarily to evert the foot. the deep peroneal nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the leg, whose muscles mainly act as dorsflexors of the foot and toes,though they also participate in some inversion. The superficial peroneal nerve gives off branches that provide sensory innervation to the majority of the dorsum of the foot while the deep peroneal nerve provides sensory innervation only to the region between the first and second digits of the foot. Injury to the common peroneal nerve from proximal fibula fracture would cause loss of sensation in both of these regions as well as motor deficits resulting in a clinical presentation with “foot drop”.
the neck of the fibula, the common peroneal nerve divides into superficial and deep branches. the superficial branch innervates the muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg, which function primarily to evert the foot. the deep peroneal nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the leg, whose muscles mainly act as dorsflexors of the foot and toes,though they also participate in some inversion. The superficial peroneal nerve gives off branches that provide sensory innervation to the majority of the dorsum of the foot while the deep peroneal nerve provides sensory innervation only to the region between the first and second digits of the foot. Injury to the common peroneal nerve from proximal fibula fracture would cause loss of sensation in both of these regions as well as motor deficits resulting in a clinical presentation with “foot drop”.
Source: USMLE World 2009












Some really prize articles on this website , saved to bookmarks .
Rattling good visual appeal on this web site , I’d value it 10 10.
Hello there, simply was aware of your blog via Google, and located that it is really informative. I’m going to watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful should you continue this in future. Many other folks shall be benefited from your writing. Cheers!